Iptables
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iP8YWcvKDr0&list=PLRRzkFBzCR3v-UefO69M7snZVzSnVlJKZ&index=1
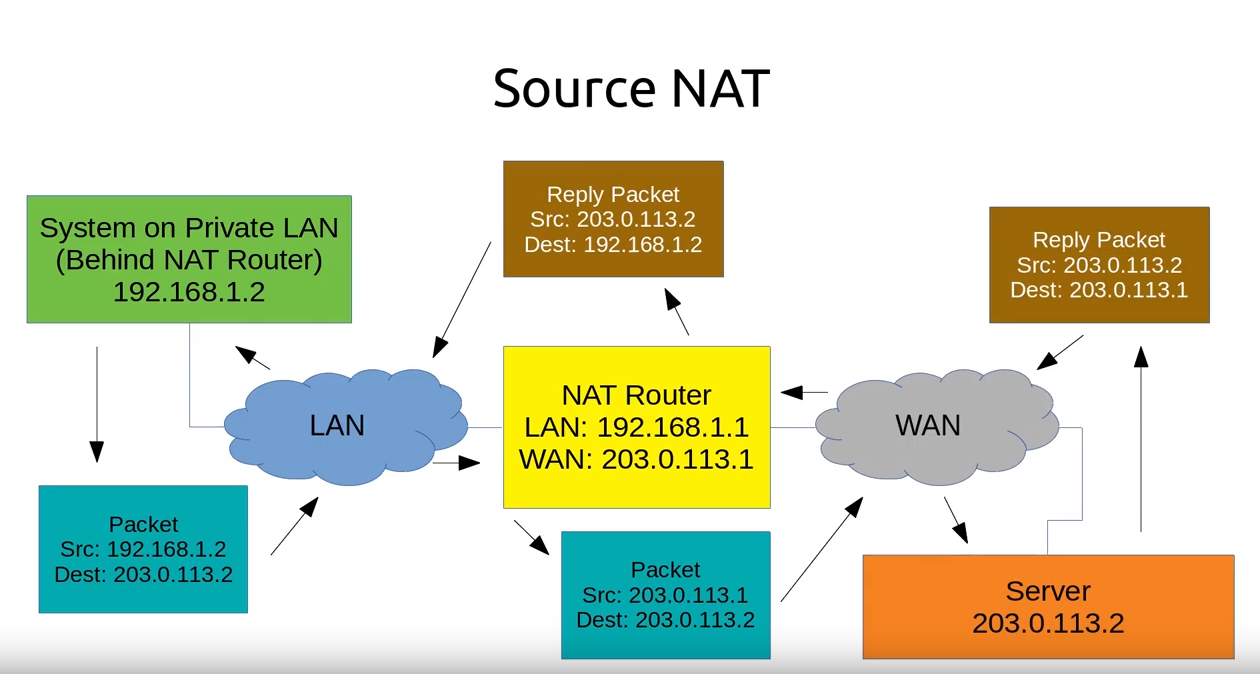
NAT
SNAT, Source NAT
- 改变 outgoing packet 的源 IP
- 跟踪链接,改变 reply packet 的目的 IP
- 可用作一组静态 IP addresses 的负载均衡
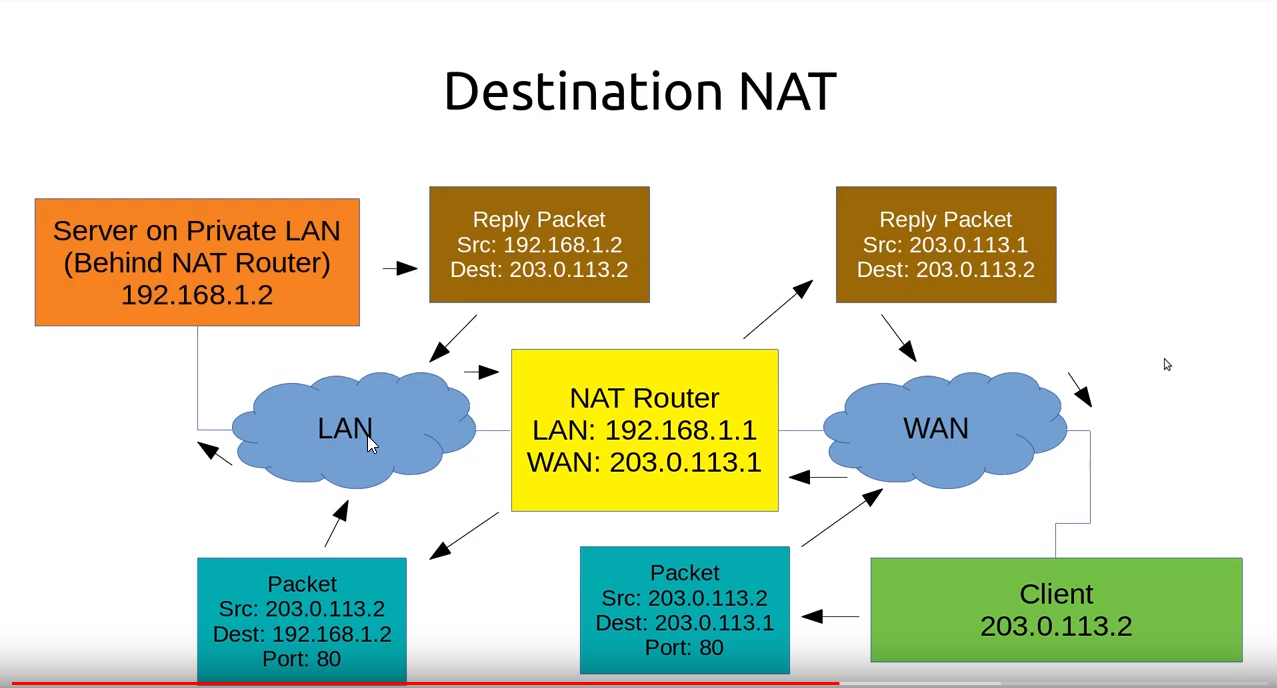
DNAT, Destination NAT
- 改变 incoming packet 的目的 IP,转发到其他设备
- 跟踪链接,改变 reply packet 的源 IP (由其他设备的源 IP 变为当前 DNAT 系统的源 IP)
通常用在 inbound packets 的端口转发
只能用在 nat table, 和 PREROUTING and OUTPUT chains
DMZ, 隔离区,DNAT 系统隔离的区域
- IP Masquerading
- A NAT route masquerades a private network
- SNAT use outgoing intreface as the address for rewriting
广泛用作 IPV4 的扩展
- private LAN using private IP address behind a NAT router, 所有流量都被视作来自 NAT router
- 所有来自private LAN 的流量都 NAT 到 NAT router 为源 IP
- 所有来自公网的流量都 NAT 处理后返回 private LAN devices
Iptables Command
1 | # -A append to `INPUT` chain |
A Basic Router
1 | A Router |
1 | *nat # nat table |
1 | *filter # filter table |
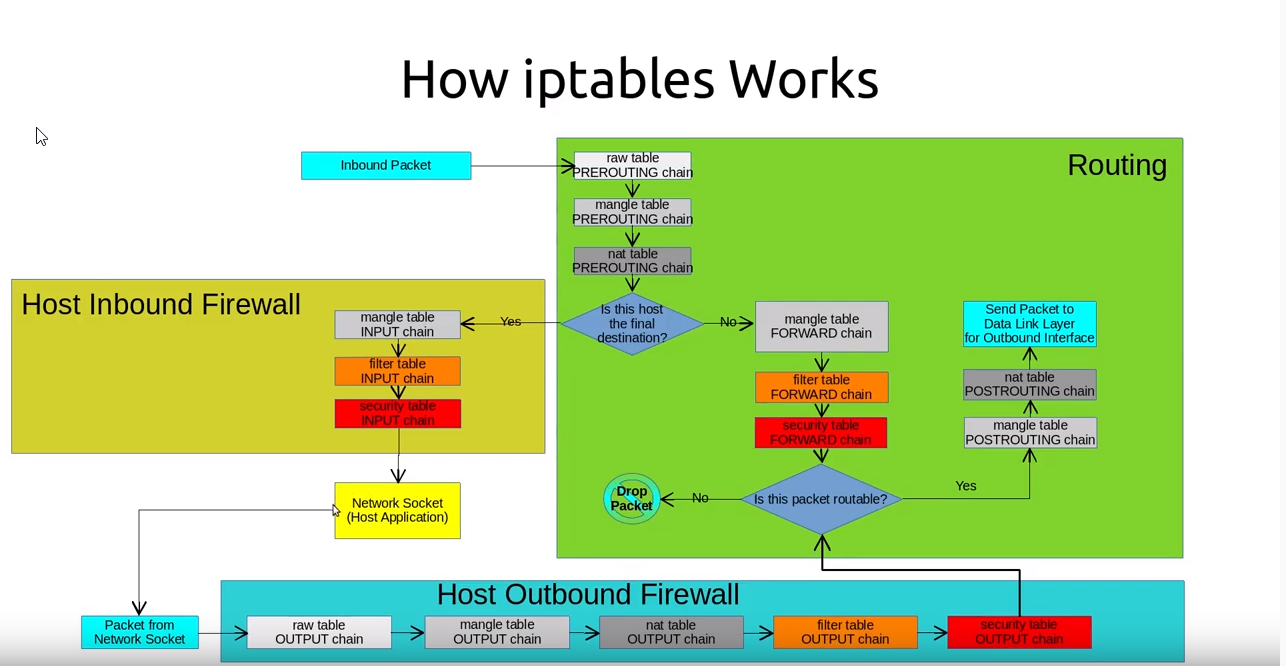
Packets Processing
Netfilter component of Linux kernel recognizes and grouped packets into streams or flows
NAT rules are only determined for the 1st packet in a stream, the all subsequent packets receive the same processing
Tables and Chains
Tables
- filter
- NAT
- mangle
- raw
- security
Chains
- PREROUTING
- INPUT
- FORWARD
- OUTPUT
- POSTROUTING
- User-defined Chains
Tables and built-in chains
Filter: Access Controls
Built-in chains
- INPUT: handles packets destined for local sockets
- FORWARD: handles packets routed through this host to another destination
- OUTPUT: handles locally generated packets
NAT: Consulted whenever a packet create a new connection
Built-in chains
- PREROUTING: alters packets arrive from the network interface
- OUTPUT: alters locally-generated packets before routing them
- POSTROUTING: alters packets about to be sent out from host
Mangle: specialized packet alteration
Built-in chains
- PREROUTING: mangling packets before routing
- OUTPUT: mangling packets before sending
- INPUT: mangling packets destined for this host
- FORWARD: mangling packets routed through the host
- POSTROUTING: mangling packets about to be sent
Security: Consulted after the filter table to implement Mandatory Access Control network rules
Built-in chains
- INPUT: packets destined for the host
- OUTPUT: packets originating from the host
- FORWARD: packets forwarded through the host
Raw: rarely used
Built-in chains
- PREROUTING: processes all incoming packets
- OUTPUT: processes outgoing packets generated by the host