Covolution Neuro Network
卷积
卷积运算,源于信号处理
感受野,接受域
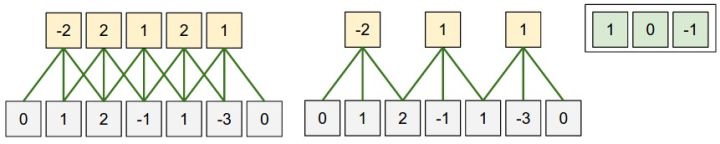
只受3个输入单元影响,接受域为3,忽略接受域外权重(无限强先验)
优点
稀疏交互
参数共享,在不同输入位置上使用相同的参数。普通神经网络权重与神经元绑定,需要 $N_l N_{l+1}$ 个参数;卷积神经网络每个权重参数不变,只需要 $kk$ 个参数。
- 平移不变性,只包含局部连接关系(接受域)

96个[11x11x3]滤波器,如果在图像某些地方探测到一个水平的边界是很重要,那么在其他一些地方也会同样是有用的,这是因为图像结构具有平移不变性。
有的滤波器学习到了条纹,有些学到了色彩差别
CNN
输出尺寸:$\frac{W-F+2P}{S} + 1$
- F: fiter, 卷积核/滤波器/感受野的尺寸,常用3x3, 5x5
- P: padding, 零填充的数量. SAME(输出与输入保持一直,p=F-1/S),VALID(不填充,输出尺寸减少, p=F/S)
- S: stride, 步长
code
1 | # forward |
卷积层是如何解决不同大小输入的问题 ???
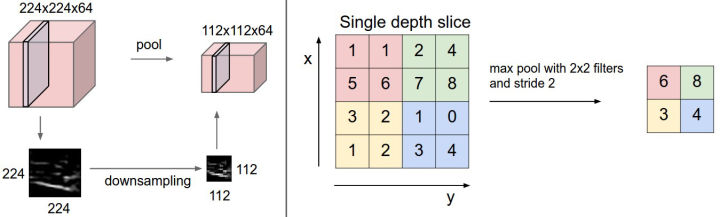
池化
特点
- 局部平移不变性:关心某个特征是否出现,不关心出现的具体位置 (无限强先验)
- 降采样:下一层少了 k 倍输入
- 综合池化区域(pool)的 k*k 个像素的统计特征
- 处理不同大小的输入,输出相同数量的统计特征
最大池化 pool (2, 2),步长 stride 2,输出大小减半
1 |
|